Les refroidisseurs à plaques Jinfan sont des équipements idéaux pour les solutions de refroidissement industriel. En tant qu'échangeur de chaleur à plaques haute efficacité, compact et démontable, il dispose d'une plaque ondulée à motif chevron unique et d'une conception en contre-courant pur, offrant ainsi une faible empreinte au sol et des capacités de refroidissement de fluide stables et fiables. Par conséquent, son efficacité de transfert de chaleur est 3 à 5 fois supérieure à celle des équipements traditionnels. Nous nous engageons à vous fournir des produits d'échange thermique adaptés à des environnements de process exigeants tels que les secteurs du chauffage, de la climatisation, de l'alimentation et des boissons, ainsi que de la marine.
Un échangeur de chaleur à plaques est un type d'échangeur de chaleur principalement utilisé pour le refroidissement de fluides. C'est un dispositif d'échange thermique très efficace qui utilise une série de plaques PHE comme milieu de transfert thermique entre les fluides. Ces plaques sont assemblées étroitement dans un cadre, formant des canaux d'écoulement étroits. Les fluides chauds et froids (comme l'eau, l'huile et la vapeur) circulent en sens opposés dans des canaux adjacents, permettant un échange de chaleur indirect et le refroidissement du fluide.
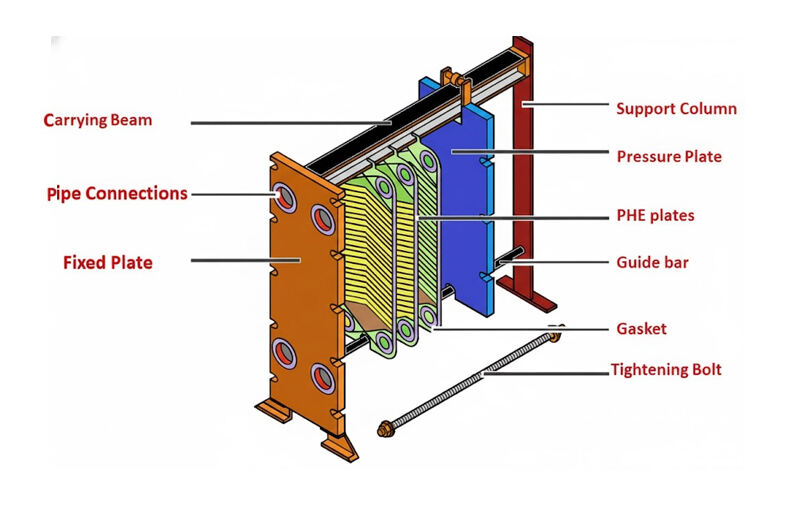
1. Plaque PHE
La plaque d'échange thermique est l'élément central de l'échangeur de chaleur à plaques, généralement fabriquée à partir de fines feuilles métalliques possédant une forte conductivité thermique et une bonne résistance à la corrosion, telles que l'acier inoxydable, le titane ou les alliages de nickel. Les plaques sont embouties avec des ondulations en chevrons uniques, qui augmentent la turbulence, améliorent l'efficacité du transfert thermique et renforcent la rigidité des plaques. Des trous sont percés aux quatre coins des plaques pour les entrées et sorties des fluides.
2. Joint d'échangeur à plaques
Le joint de l'échangeur de chaleur à plaques est installé dans la rainure d'étanchéité de chaque plaque et est généralement fabriqué en caoutchouc (tel que NBR, EPDM ou caoutchouc fluoré). Il dirige alternativement le fluide vers différents canaux d'écoulement. Le joint est une pièce consommable nécessitant un entretien ou un remplacement régulier.
3. Bâti d'échangeur à plaques
Le châssis de l'échangeur thermique à plaques se compose d'une plaque fixe de serrage, d'une plaque mobile de serrage, d'une tige supérieure de guidage, d'une tige inférieure de guidage et de boulons de serrage. Son rôle est de comprimer l'ensemble des plaques et joints afin de former un ensemble étanche et de supporter la pression de service du fluide.
Le fluide chaud pénètre par un orifice de l'équipement et est dirigé, via la distribution des trous d'angle des plaques, vers le canal d'écoulement formé par les intervalles impairs entre les plaques. L'eau de refroidissement entre par l'autre orifice et est dirigée vers le canal d'écoulement adjacent formé par les intervalles pairs entre les plaques. Les deux fluides circulent en sens opposés dans des canaux d'écoulement étroits et adjacents. La chaleur est transférée du fluide à température plus élevée à travers les plaques métalliques minces vers le fluide à température plus basse. Le fluide refroidi s'écoule par un autre orifice d'huile, tandis que le fluide ayant absorbé la chaleur s'écoule par un autre orifice d'eau. Les deux fluides ne sont jamais en contact au cours de l'ensemble du processus ; il s'agit d'un échange thermique purement indirect.
Haut rendement : Le coefficient de transfert thermique est 3 à 5 fois supérieur à celui des échangeurs de chaleur traditionnels à tubes et à calandre.
Entretien facile : Les boulons peuvent être facilement desserrés pour ouvrir l'appareil, permettant un nettoyage mécanique, une inspection, ou l'ajout ou le retrait de plaques d'échange thermique afin d'ajuster la capacité.
Grande flexibilité : La surface d'échange thermique et la capacité peuvent être facilement ajustées en augmentant ou en diminuant le nombre de plaques, afin de s'adapter à différentes exigences de procédé.
Faibles pertes thermiques : La structure compacte permet un échange de chaleur maximal, avec une dissipation minimale de chaleur vers l'environnement.
Petite différence logarithmique moyenne de température : Grâce à une véritable contre-courant, un échange thermique efficace peut être réalisé avec de faibles écarts de température, et une forte capacité de récupération de la chaleur résiduelle basse température.
× Résistance limitée en pression et température : En raison des limitations liées au joint d'étanchéité et au matériau des plaques, la pression de fonctionnement typique ne dépasse pas 2,5-3,0 MPa, et la température générale de fonctionnement ne dépasse pas 180-200 °C (des pressions plus élevées sont possibles avec des matériaux de joints spéciaux).
√ L'échangeur de chaleur à plaques sans joints entièrement soudé de JINFAN est conçu pour des pressions plus élevées et peut fonctionner à des températures supérieures à 300 °C.
× Sensible à l'obstruction : Les canaux d'écoulement sont très étroits, et un colmatage peut facilement survenir si le fluide contient de grosses particules solides ou des fibres. Un filtre est généralement requis à l'entrée.
√ L'échangeur de chaleur à plaques à grand écart JINFAN présente un design unique de plaques ondulées, permettant une manipulation fluide des matières particulaires (telles que les eaux usées, la pâte à papier, le sirop, les boues, etc.) et réduisant considérablement le risque de colmatage.
Les échangeurs à plaques servent d'échangeurs thermiques primaires et secondaires dans les stations énergétiques centrales, distribuant efficacement de l'eau chaude/froide vers divers bâtiments.
L'échangeur à plaques est utilisé pour la pasteurisation, la stérilisation éclair et le refroidissement rapide des aliments liquides, en vue de leur conditionnement en continu.
Le refroidisseur d'huile à plaques dans les unités principales et les boîtes de réduction assure une température d'huile stable et garantit le fonctionnement stable à long terme des grands équipements tournants.