Jinfan Plate type Coolers are ideal heat exchange equipment for industrial cooling solutions. As a high-efficiency, compact, and detachable plate heat exchanger, it features a unique herringbone corrugated plate and a pure counter-flow design, resulting in a small footprint and stable, reliable fluid cooling capabilities. Therefore, its heat transfer efficiency is 3-5 times higher than traditional equipment. We are committed to providing you with heat exchange products suitable for demanding process environments such as HVAC, food and beverage, and marine industries.
A plate heat exchanger is a type of plate heat exchanger primarily used for cooling media. It is a highly efficient heat exchange device that utilizes a series of PHE plates as the fluid heat transfer medium. The plates are tightly assembled within a frame, forming narrow flow channels. Hot and cold fluids (such as water, oil, and steam) flow in opposite directions in adjacent channels, generating indirect heat exchange and cooling the fluid medium.
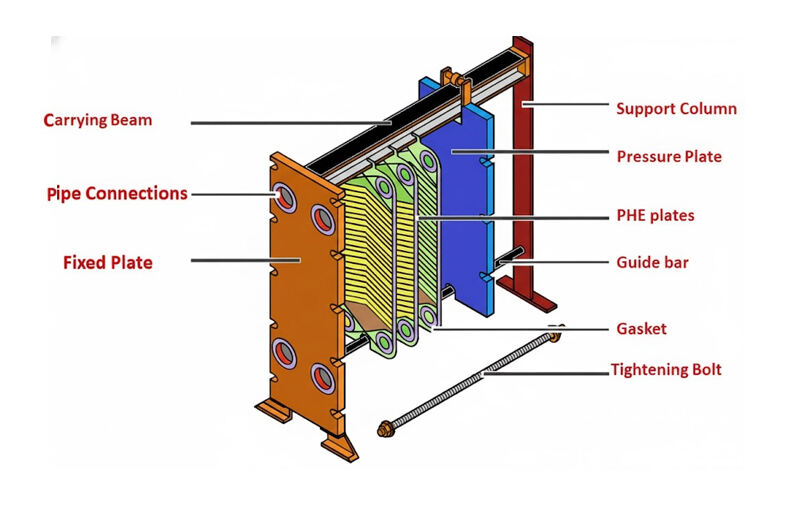
1. PHE Plate
The plate heat exchange plate is the core component of the plate heat exchanger, typically made of thin metal sheets with high thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, such as stainless steel, titanium, or nickel alloys. The plates are stamped with unique herringbone corrugations, which enhance turbulence, improve heat transfer efficiency, and increase plate rigidity. Holes are opened at the four corners of the plates for fluid inlets and outlets.
2. PHE Gasket
The plate heat exchanger gasket is installed in the sealing groove of each plate and is usually made of rubber (such as NBR, EPDM, or fluororubber). It guides the fluid alternately into different flow channels. The gasket is a consumable part and requires regular maintenance or replacement.
3. PHE Frame
The plate heat exchanger frame consists of a fixed clamping plate, a movable clamping plate, an upper guide rod, a lower guide rod, and clamping bolts. Its function is to press all the plates and gaskets together to form a sealed unit and withstand the working pressure of the fluid.
The hot medium enters from one port of the equipment and is guided through the distribution of the plate corner holes into the flow channel formed by the odd number of plate gaps. Cooling water enters from the other port and is guided into the adjacent flow channel formed by the even number of plate gaps. The two fluids flow in opposite directions in adjacent narrow flow channels. Heat is transferred from the higher-temperature medium through the thin metal plates to the lower-temperature medium. The cooled medium flows out from the other oil port, while the medium that has absorbed heat flows out from the other water port. The two fluids do not come into contact at all during the entire process; it is a purely indirect heat exchange.
High Efficiency: The heat transfer coefficient is 3-5 times that of traditional shell-and-tube heat exchangers.
Easy to maintain: Bolts can be easily loosened to open for mechanical cleaning, inspection, or to add or remove PHE Plates to adjust capacity.
High flexibility: The heat exchange area and capacity can be easily adjusted by increasing or decreasing the number of plates to adapt to different process requirements.
Low heat loss: The compact structure allows for maximum heat exchange, with minimal heat dissipation to the environment.
Small logarithmic mean temperature difference: Due to true counterflow capability, effective heat exchange can be achieved with small temperature differences, and strong ability to recover low-temperature waste heat.
× Limited pressure and temperature resistance: Due to gasket sealing and plate material limitations, the typical operating pressure does not exceed 2.5-3.0 MPa, and the general operating temperature does not exceed 180-200°C (higher pressures are possible with special gasket materials).
√ JINFAN's gasketless, all-welded plate heat exchanger is designed for higher pressures and can operate at temperatures exceeding 300°C.
× Prone to clogging: The flow channels are very narrow, and clogging can easily occur if the fluid contains large solid particles or fibers. A filter is usually required at the inlet.
√ The JINFAN Wide Gap Plate Heat Exchanger features a unique corrugated plate design, enabling smooth handling of particulate matter (such as wastewater, pulp, syrup, sludge, etc.) and significantly reducing the risk of clogging.
Plate Coolers serve as primary and secondary heat exchangers in central energy stations, efficiently distributing hot/cold water to various buildings.
PHE Cooler is used for pasteurization, flash sterilization, and rapid cooling of liquid foods, preparing them for continuous filling.
Plate Oil Cooler in main units and reduction gearboxes ensures stable oil temperature and guarantees long-term stable operation of large rotating equipment.